Hospital Bench Marking
Home » Hospital Bench Marking
Hospital Bench Marking
Hospital benchmarking is a strategic management tool that involves comparing a hospital’s performance metrics with those of other healthcare institutions to identify best practices, areas for improvement, and opportunities for enhanced efficiency and effectiveness. Benchmarking helps hospitals set performance standards, track progress, and achieve continuous improvement. Here are key aspects of hospital benchmarking:
Performance Metrics:
Identify and define the key performance indicators (KPIs) that are crucial for assessing hospital performance. These may include patient outcomes, financial metrics, operational efficiency, patient satisfaction, and quality of care indicators.
Peer Comparison:
Select peer hospitals or healthcare institutions with similar characteristics, such as size, patient population, geographic location, and service offerings. Comparing performance with relevant peers provides a more accurate and meaningful assessment.
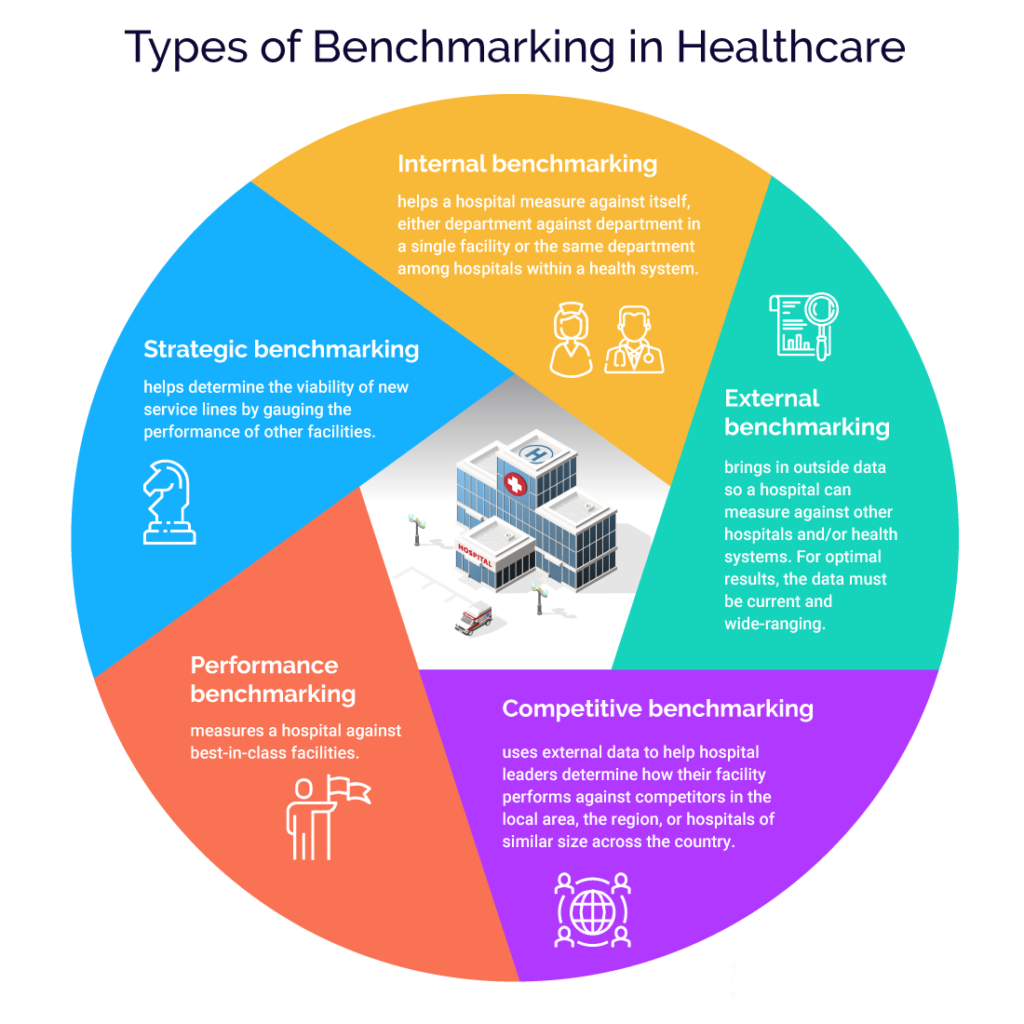
Data Collection and Analysis:
Gather relevant data for the chosen performance metrics from internal sources, external databases, or industry reports. Ensure that the data is accurate, reliable, and comparable across institutions. Use statistical tools and methods for data analysis.
Identifying Best Practices:
Benchmarking allows hospitals to identify best practices in areas where peer institutions outperform. Analyzing these practices helps hospitals understand how they can improve their processes and outcomes.
Setting Benchmarks and Targets:
Establish benchmarks based on the performance of top-performing peer institutions. These benchmarks serve as targets for improvement, helping hospitals set realistic goals and measure progress over time.
Operational Efficiency:
Evaluate operational processes to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. This may include examining workflow, resource utilization, patient throughput, and other operational aspects to enhance efficiency.
Financial Performance:
Assess financial metrics such as revenue per patient, cost per case, and operating margins in comparison to peer institutions. Identifying areas for financial improvement ensures the long-term sustainability of the hospital.
Patient Outcomes and Safety:
Compare patient outcomes and safety metrics, including mortality rates, readmission rates, and infection rates. Understanding how peer institutions achieve better outcomes guides hospitals in enhancing patient care.
Patient Satisfaction:
Analyze patient satisfaction scores and feedback compared to peer institutions. Identifying areas of improvement in patient experience helps hospitals enhance the quality of care and patient engagement.
Strategic Planning:
Use benchmarking insights to inform strategic planning. Identify priorities, allocate resources effectively, and align organizational goals with the best practices observed in high-performing peer institutions.
Continuous Monitoring:
Hospital benchmarking is an ongoing process. Regularly monitor and update benchmarks to reflect changes in the healthcare landscape, technology, and patient demographics. Continuous monitoring ensures that hospitals remain agile and responsive to evolving challenges.
Share and Learn:
Establish a culture of sharing benchmarking results and lessons learned across departments and with relevant stakeholders. This promotes a collaborative approach to improvement and innovation within the hospital.
Hospital benchmarking is a dynamic and iterative process that contributes to the continuous improvement of healthcare services. By learning from peers, identifying best practices, and setting realistic targets, hospitals can enhance their performance, deliver higher quality care, and ultimately improve patient outcomes.
Ready to Begin?
Start with our FREE Consultation!
Or call +880 1766-709223 or write us at info@qcconcern.org with any other questions.
