Quality ICU monitoring tools
Home » Quality ICU monitoring tools
Quality ICU monitoring tools
Monitoring critically ill patients in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is a complex task that requires sophisticated tools to track vital signs, assess organ function, and respond to changes promptly. Quality ICU monitoring tools play a crucial role in enhancing patient safety and improving outcomes. Here are key components of quality ICU monitoring tools:
Multiparameter Monitors:
Multiparameter monitors integrate various monitoring parameters, such as electrocardiography (ECG), blood pressure, oxygen saturation, respiratory rate, and temperature. These comprehensive systems provide real-time data on a single display, facilitating continuous patient assessment.
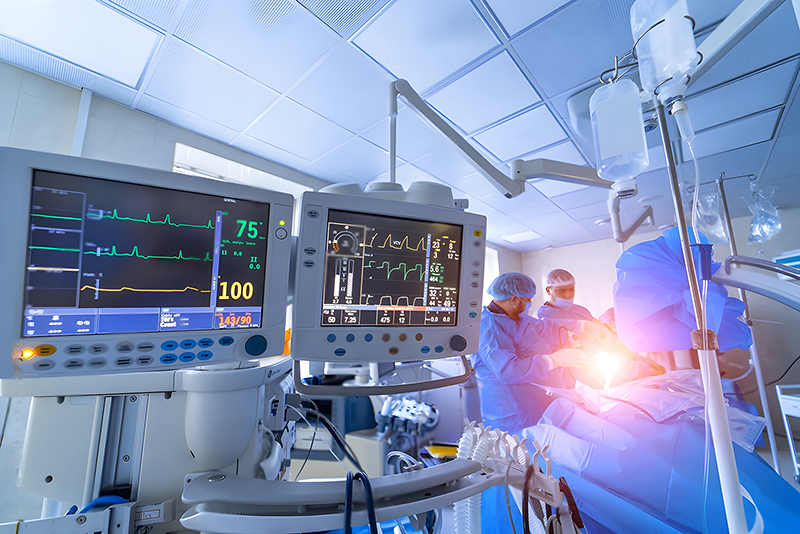
Hemodynamic Monitoring:
Hemodynamic monitoring tools assess the function of the cardiovascular system. This includes tools for measuring central venous pressure (CVP), pulmonary artery pressure (PAP), and cardiac output. Hemodynamic monitoring aids in managing fluid balance and optimizing cardiovascular support.
Ventilator Monitoring:
For mechanically ventilated patients, ventilator monitoring tools are essential. These tools track parameters like tidal volume, respiratory rate, positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), and inspiratory oxygen concentration. They help optimize ventilator settings and assess lung mechanics.
Continuous Electroencephalogram (EEG) Monitoring:
Continuous EEG monitoring is crucial for assessing brain activity in patients at risk of neurological complications. This tool is particularly important for patients with traumatic brain injuries, seizures, or those undergoing therapeutic hypothermia.
Continuous Pulse Oximetry:
Continuous pulse oximetry measures oxygen saturation levels in the blood, providing a real-time assessment of respiratory function. It is a vital tool for identifying hypoxemia and ensuring adequate oxygenation.
Capnography:
Capnography monitors end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in exhaled breath. It is valuable for assessing ventilation, detecting respiratory compromise, and guiding ventilator management.
Invasive Blood Pressure Monitoring:
Invasive blood pressure monitoring involves placing arterial catheters to directly measure blood pressure. This provides accurate and continuous data, particularly for patients with hemodynamic instability.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring:
Monitoring glucose levels in critically ill patients is essential, especially for those with sepsis or on parenteral nutrition. Continuous glucose monitoring tools offer real-time data and help guide insulin therapy.
Renal Function Monitoring:
Tools for monitoring renal function include serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and urine output monitoring. These parameters are crucial for assessing kidney function and guiding fluid management.
Temperature Monitoring:
Continuous temperature monitoring tools track core body temperature, which is essential for patients at risk of hyperthermia or hypothermia. This is particularly important in critically ill patients, especially those undergoing therapeutic hypothermia.
Point-of-Care Ultrasound (POCUS):
POCUS is a valuable tool for real-time imaging at the bedside. It is used for assessing cardiac function, lung status, and guiding various procedures in the ICU.
Electronic Health Records (EHRs) Integration:
Integration with EHRs ensures that the data collected by monitoring tools is seamlessly documented and easily accessible to the healthcare team. This supports comprehensive patient care and facilitates data-driven decision-making.
Alarm Systems with Smart Notifications:
Advanced alarm systems with smart notifications help reduce alarm fatigue by prioritizing critical alarms and providing timely alerts to healthcare providers for prompt intervention.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring:
Telemedicine platforms and remote monitoring tools allow healthcare providers to monitor ICU patients from a distance. This is particularly useful for surveillance, early detection of deterioration, and efficient use of resources.
Data Analytics and Decision Support:
Data analytics tools analyze large volumes of patient data to identify trends, predict potential issues, and provide decision support. These tools can assist in early identification of deteriorating patients and support evidence-based care.
The integration of these quality ICU monitoring tools contributes to a comprehensive and dynamic approach to patient care, allowing healthcare providers to respond promptly to changes in patient status and optimize treatment strategies. It’s essential to regularly update and optimize these tools to ensure they align with the latest standards and technologies.
Ready to Begin?
Start with our FREE Consultation!
Or call +880 1766-709223 or write us at info@qcconcern.org with any other questions.
