Transforming Healthcare: Lessons and Best Practices for Sustainable Health System Reforms
Healthcare system reforms are crucial for improving access, quality, and sustainability. Drawing from global experiences, several best practices and key lessons have emerged that offer valuable insights for creating sustainable health systems. By adopting these practices, countries can improve healthcare delivery, financing, governance, and overall patient outcomes.
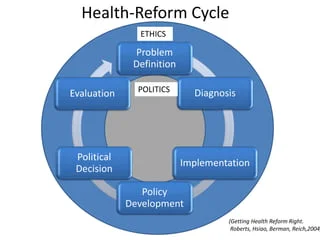
Key Lessons from Best Practices in Health System Reform
a. Policy and Governance
- Strong Leadership and Political Will: Successful health reforms require unwavering commitment from government leaders. For example, Thailand’s Universal Health Coverage (UHC) was made possible through a strong government focus on health as a national priority.
- Evidence-Based Policies: Policymaking should be grounded in solid research and data. Rwanda’s community-based insurance model is a great example of how evidence-driven policies can ensure inclusivity and effectiveness.
- Clear Accountability: Effective governance with transparent structures ensures smooth implementation and monitoring of reforms, preventing corruption and inefficiency.
b. Financing Models
- Sustainable Funding Sources: Countries like the UK fund their National Health Service (NHS) through taxation, securing long-term financial sustainability for healthcare systems.
- Equity in Financing: Ensuring the poorest populations are not burdened by healthcare costs is essential. Thailand’s UHC has successfully reduced out-of-pocket healthcare spending, providing a model for equity in financing.
c. Healthcare Delivery
- Primary Care Focus: Reforms such as Brazil’s Family Health Strategy emphasize the importance of strengthening primary care as the first point of contact, improving accessibility and efficiency in the system.
- Integration of Services: Effective reforms coordinate healthcare services at primary, secondary, and tertiary levels, ensuring comprehensive care and better patient outcomes.
- Digital Health Integration: Countries like Estonia have implemented digital health platforms, improving healthcare efficiency and access through innovative technological solutions.
d. Stakeholder Engagement
- Community Participation: Actively involving communities in healthcare reform ensures the adoption of culturally appropriate and accepted solutions.
- Collaborative Approach: Collaborations with NGOs, the private sector, and international organizations amplify the impact of health reforms, ensuring greater reach and effectiveness.
e. Monitoring and Evaluation
- Continuous Learning: Ongoing evaluation based on performance metrics allows health systems to adapt and improve over time.
- Innovation and Flexibility: Piloting new models and scaling up successful innovations fosters sustainable progress and adaptability in health systems.
Reciting Learnings for the Future: Ensuring Sustainable Health System Reforms
To build on these successful practices, it’s essential to ensure that valuable lessons are preserved and used effectively for future health reforms.
a. Documenting Case Studies
- Develop a repository of case studies showcasing successful health reforms, their strategies, and the challenges they faced.
b. Institutional Memory
- Establish knowledge-sharing platforms within healthcare organizations to facilitate the sharing of insights and experiences across different reforms.
c. Training and Capacity Building
- Integrate global best practices into training programs for policymakers, healthcare leaders, and practitioners to ensure a well-prepared workforce.
d. Advocacy and Awareness
- Use evidence from successful reforms to advocate for similar approaches in other regions, emphasizing the social and economic benefits of health system improvements.
e. Digital Knowledge Archives
- Create online tools or apps to consolidate knowledge, frameworks, and performance metrics from global health reform initiatives.
f. Networking and Collaboration
- Encourage international networking and collaboration with health organizations to continuously exchange insights and adapt global innovations.
Suggested Approach for Future Health Reforms
To build adaptable and resilient health systems, future reforms should focus on incremental changes that are customized to local contexts rather than large-scale overhauls. Key strategies include:
- Transparency and Community Engagement: Building trust through openness and active community participation ensures acceptance and long-term success of reforms.
- Technology Investment: Leveraging technology for data collection, monitoring, and service delivery will enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare systems.
- Pilot and Scale Innovations: Establish mechanisms for piloting new ideas based on evidence and scaling successful innovations to larger populations.
By adopting these practices, health systems can become more adaptive and resilient, capable of meeting the evolving needs of their populations.
For further details on specific reforms and strategies, tools like the WHO Health Systems Framework or case studies from the International Journal for Equity in Health offer additional insights into global health system best practices.