Exploring Alternatives to SWAP for Bangladesh’s Health Sector: A Path Towards Sustainable Healthcare
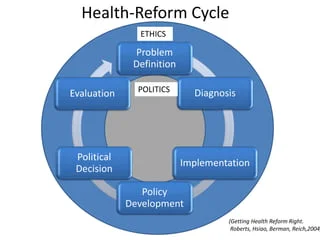
The Sector-Wide Approach (SWAP) has contributed to better donor coordination and alignment of resources with Bangladesh’s national health priorities. However, SWAP now faces challenges such as financial inefficiencies, limited flexibility, and sustainability concerns. To build a resilient health sector, alternative financing models must be explored. Public-Private Partnerships (PPP), national health insurance, and outcome-based funding are potential solutions for sustainable healthcare in Bangladesh.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) could enhance healthcare infrastructure by leveraging private investments, while national health insurance would protect citizens from high out-of-pocket expenses. Outcome-based funding models ensure resources are allocated based on measurable health outcomes, promoting efficient investments.
The government’s role in developing policies for these alternatives, with support from development partners and international agencies, is crucial. Key steps include stakeholder consultations, pilot programs, and continuous monitoring to ensure these models succeed.
Conclusion: Reforming Bangladesh’s health financing system requires integrating SWAP with innovative solutions to promote long-term financial sustainability and equitable healthcare access.
Keywords: Bangladesh health sector, SWAP alternatives, Public-Private Partnerships, national health insurance, outcome-based funding, health financing reform, sustainable healthcare