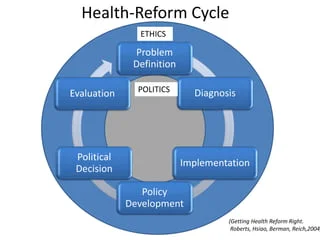
The Mandate for a New Act: Ensuring Health System Reform and Achieving Universal Health Coverage in Bangladesh:
Introduction
Universal Health Coverage (UHC) aims to ensure that all individuals and communities receive the health services they need without suffering financial hardship. Achieving UHC requires comprehensive health system reform, which in turn necessitates the establishment of a new legal framework. A new act or law is essential to institutionalize changes, allocate resources, and ensure accountability. Here’s why a new law is mandatory for health system reform to achieve UHC in Bangladesh.
Establishing a Legal Foundation
Codifying UHC Goals
A new law can formally enshrine the goals of UHC into the national legal framework, making it a binding obligation for the government to work towards these objectives. This ensures a long-term commitment to UHC beyond changes in political leadership.
Standardizing Care and Access
The law can establish uniform standards for health services, ensuring that all citizens receive a consistent level of care. This is crucial for reducing disparities in health service delivery across different regions and populations.
Ensuring Sustainable Funding
Dedicated Financing Mechanisms
A new act can create dedicated financing mechanisms for health services, such as health insurance schemes, taxes, or subsidies. This ensures a steady and sustainable flow of funds necessary to support UHC initiatives.
Financial Protection for Citizens
The law can mandate financial protection measures, such as caps on out-of-pocket expenses and the establishment of social safety nets, to prevent individuals from falling into poverty due to healthcare costs.
Enhancing Governance and Accountability
Clear Roles and Responsibilities
A new law can delineate the roles and responsibilities of various stakeholders, including government agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations. This clarity helps in effective coordination and implementation of health services.
Transparency and Accountability Mechanisms
The act can introduce mechanisms for monitoring and accountability, such as independent oversight bodies and regular public reporting. This ensures transparency in how resources are used and health services are delivered, fostering public trust.
Improving Health Service Delivery
Regulation and Quality Control
The law can establish regulatory frameworks for healthcare providers, ensuring adherence to quality standards and ethical practices. This is crucial for maintaining high standards of care and patient safety.
Incentives for Health Professionals
A new act can include provisions for training, incentives, and career development for health professionals, addressing workforce shortages and enhancing the quality of care.
Promoting Equity and Inclusivity
Access for Marginalized Groups
The law can mandate specific measures to ensure that marginalized and vulnerable groups have equitable access to health services. This includes provisions for rural health services, gender-specific care, and support for disabled individuals.
Addressing Social Determinants of Health
The act can incorporate policies addressing social determinants of health, such as education, housing, and nutrition, which are critical for achieving UHC.
Facilitating Technological Integration
Digital Health Framework
A new law can provide a legal framework for the adoption of digital health technologies, including telemedicine, electronic health records, and health information systems. This integration is vital for improving access, efficiency, and quality of care.
Data Privacy and Security
The law can establish robust data privacy and security measures, ensuring that personal health information is protected as digital health solutions are implemented.
Conclusion
A new act or law is mandatory for health system reform to achieve the goal of Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in Bangladesh. It provides a legal foundation for codifying UHC goals, ensuring sustainable funding, enhancing governance and accountability, improving service delivery, promoting equity and inclusivity, and facilitating technological integration. By establishing clear, enforceable legal frameworks, the government can ensure that health system reforms are comprehensive, coordinated, and sustainable, ultimately leading to the successful achievement of UHC for all citizens.